We have heard about the throw and throws keyword in Exception handling, which tends to be an important part of handling an exception.
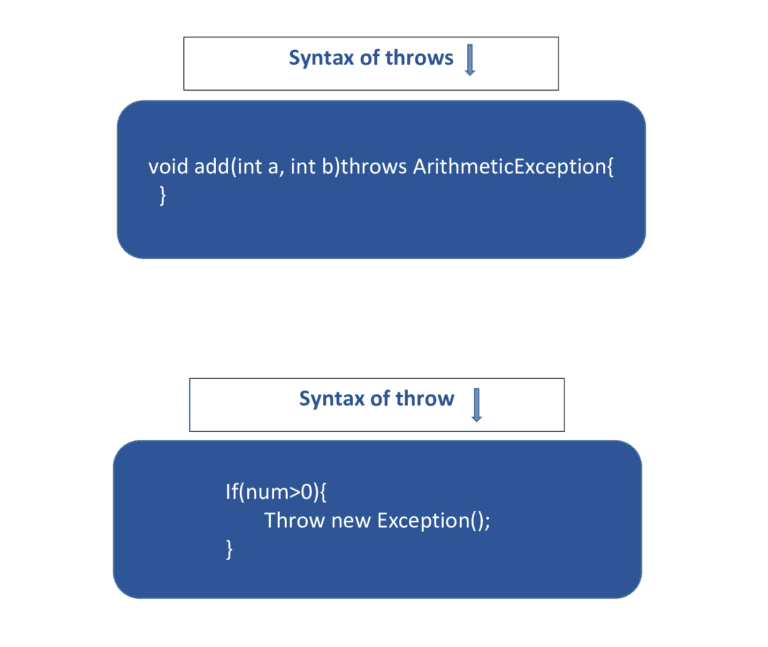
The above diagram clearly explains the throw and throws keyword and now let’s discuss the differences between throw and throws.
Throw
Throws
Now let us see the basic example of the throw and throws keyword.
//throws keyword example
package multipleCatch;
public class Multiple{
public static void main(String[] args)throws ArithmeticException {
int a=5,b=0,c;
try {
c=a/b;
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("exception is "+e);
}
}
}
//throw keyword example
package multipleCatch;
public class Multiple{
int a=5,b=0,c;
void checkException() {
c=a/b;
try {
throw new ArithmeticException("not allowed");
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Multiple multiple=new Multiple();
multiple.checkException();
}
}
Feel free to try this example and comment below.
Copyright ©TechOceanhub All Rights Reserved.